About Us
Telemedicine has evolved far beyond its initial role as a pandemic stopgap, establishing itself as a permanent and transformative care channel, with telehealth utilization stabilizing at ~38× pre‑pandemic levels, even after the initial surge subsided.
For healthcare leaders and investors, telemedicine statistics reveal how this innovation is reshaping the way health systems attract patients, manage chronic conditions, and optimize clinical capacity.
As telemedicine continues to expand, this article will explore key growth areas within telemedicine, virtual care platforms, and remote patient monitoring (RPM). By leveraging telemedicine statistics and data-driven insights, we’ll highlight the most promising investment opportunities and provide guidance on where to allocate resources in this rapidly expanding market.
Telemedicine is a large and rapidly growing market, with strong growth projected through 2030. Market research consistently shows a positive trajectory:
The key factors driving adoption include:
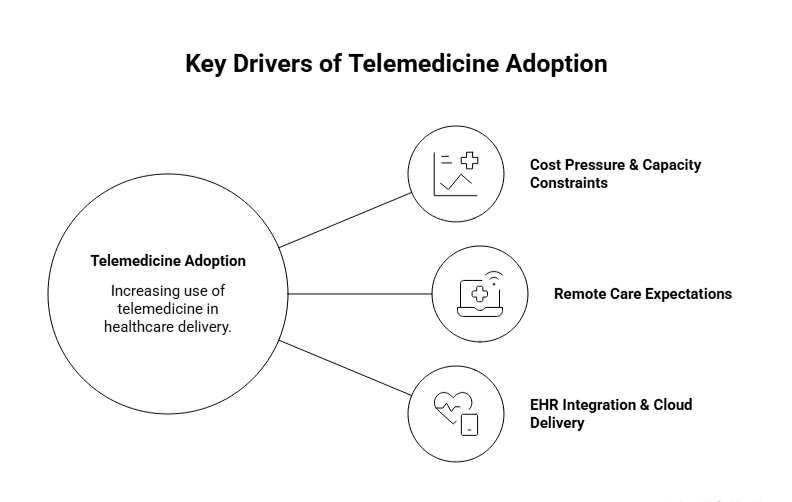
Telemedicine is increasingly integrated into electronic health record (EHR) workflows and hybrid care models, shifting away from being viewed as a standalone service. This integration is a major catalyst for APIs, identity management, scheduling tools, documentation, and revenue-cycle solutions.
Telemedicine adoption has shifted from a temporary solution to a permanent, mainstream care model.
Let’s explore the trends in provider adoption, utilization patterns, and key areas driving sustained demand post-COVID:
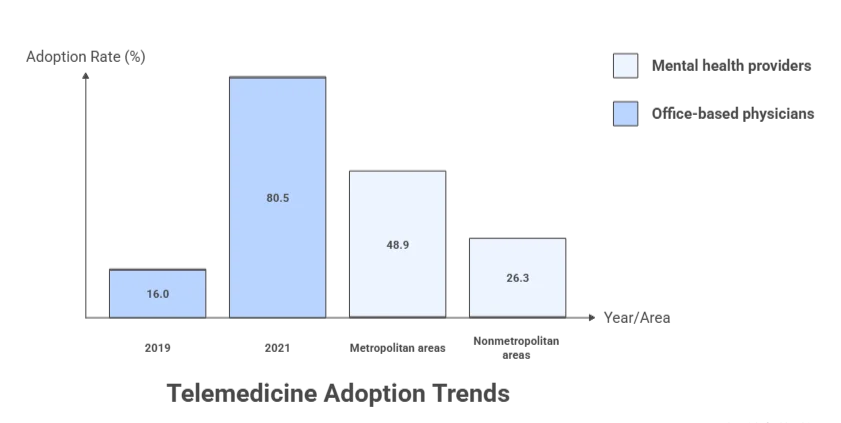
One of the most telling signs of telemedicine’s long-term potential is its widespread adoption among healthcare providers. In the U.S., the share of office-based physicians using telemedicine for patient care surged from 16.0% in 2019 to 80.5% in 2021. This isn’t just “pilot” adoption; it reflects a significant shift in institutional behavior.
Although telemedicine utilization has dipped from its pandemic peak, it remains consistently higher than pre-COVID levels. According to FAIR Health, U.S. telehealth utilization rose from 4.74% of medical claims in July 2024 to 5.04% in December 2024.
Behavioral health continues to be the dominant use case for telemedicine. Between July and December 2024, mental health conditions accounted for 66-67% of telehealth claim lines, solidifying it as the most persistent and in-demand telehealth service.
Data from AHRQ/MEPS reveals a persistent gap in telehealth access between metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas. For mental health providers, telehealth adoption was 48.9% in metropolitan areas, but only 26.3% in nonmetropolitan areas. This gap presents a significant product opportunity for telehealth solutions designed for low-bandwidth or hybrid modalities.
The financial impact of telemedicine goes beyond basic cost savings. Let’s explore the most defensible ROI opportunities, the broader virtualization potential, and the latest trends in venture funding.
While telemedicine app development costs can be substantial, the ROI of telemedicine is most effectively realized through indirect savings, particularly from reductions in time, travel, and missed work, as well as improvements in operational efficiency. Rather than direct revenue generation, these factors contribute significantly to long-term cost reductions, making the financial benefits more defensible.
A notable economic evaluation in oncology found that:
Telehealth visits saved an average of $147–$186 per visit.
For new or established visits, savings ranged from $176.6 to $222.8, depending on mileage and travel distances.
McKinsey estimates that up to $250B of U.S. healthcare spend could potentially shift to virtual or virtually enabled care. This figure serves as a useful benchmark for investors, signaling the size of the opportunity if workflows and reimbursement frameworks align.
While this is not a guarantee, it sets a clear boundary on the potential size of the market.
Although digital health funding has cooled since the 2021 peak, capital is still being invested, particularly in AI-driven operational tools. In 2024, U.S. digital health venture funding totaled $10.1B across 497 deals.
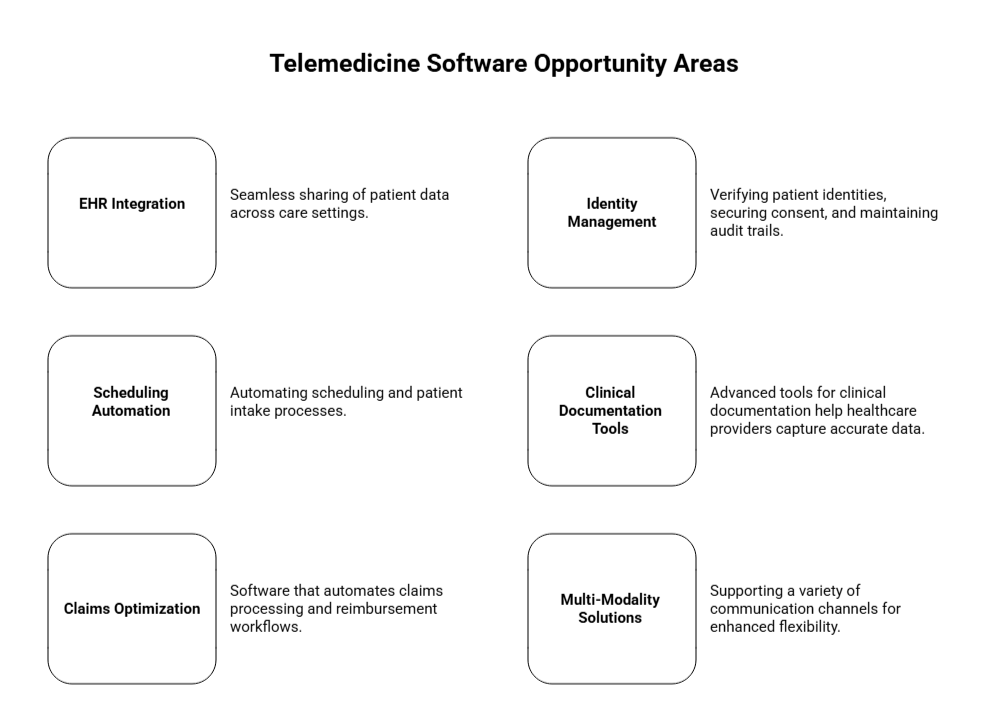
Telemedicine platforms are evolving quickly, with cloud delivery and seamless integration becoming standard. Here’s how the key technologies are driving growth, expanding RPM market, and the critical software features that make platforms scalable and secure.
As these platforms expand, telemedicine app features like cloud-based delivery and seamless integration are becoming essential for scalability and efficiency. According to Grand View Research, the telehealth software market is experiencing strong growth, driven by the increasing demand for healthcare IT solutions and cloud-based infrastructure.
RPM is becoming an integral part of virtual care programs, especially for chronic diseases, hospital-at-home, and post-acute care. The RPM market is projected to grow from $27.72B in 2024 to $56.94B by 2030, reflecting a 12.7% CAGR.
For U.S.-based platforms, HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable. HHS telehealth guidance sets the standard for both product design and vendor selection, ensuring platforms meet privacy and security requirements.
Key areas of investment in telemedicine software include:
Patient satisfaction with telehealth services is generally positive but varies by provider. J.D. Power reports:
| Telehealth Type | Satisfaction Score (out of 1000) | Year-over-Year Change | Barrier Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-to-consumer Telehealth | 730 | Down 1 point | – |
| Payer-provided Telehealth | 708 | Up 18 points | – |
| Patients Facing Barriers | – | – | 65% |
A 2024 Doximity report shows broad clinician support for telemedicine:
Though this is the best time to invest in telemedicine, there sure are some areas you must consider when taking the final decision, they include:
Medicare remains a critical policy driver for telehealth adoption. CMS has extended telehealth flexibility for Medicare beneficiaries through January 30, 2026, with changes starting for non-behavioral services on January 31, 2026.
AHRQ data highlights the rural/metro gap in telehealth access, particularly for mental health services.
Only 37% of European countries report evaluating their telehealth services, according to the WHO Europe survey. This indicates a significant gap in measurement and outcomes tracking.
Telemedicine is no longer just a stopgap measure. By 2026, it has solidified its place as a core, multifaceted component of healthcare delivery. This transition reflects not only widespread adoption but a rethinking of how technology can drive efficiency and continuity of care across patient and provider touchpoints.
Telemedicine is transitioning from a niche solution to a central pillar of healthcare delivery. The most promising growth areas are in care models supported by advanced software rather than just video visits. For developers and healthcare providers, understanding these emerging trends is crucial, and a solid telemedicine app development guide can help ensure your platform remains adaptable and competitive.
Key Trends to Watch:
Hybrid Care Pathways: The integration of virtual and in-person care is becoming the norm. This model ensures continuity and flexibility for patients while optimizing resource utilization for providers.
Chronic Care Programs with RPM: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is increasingly bundled with chronic care management programs, enabling better long-term management of conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. These programs are poised to scale as patients seek ongoing, remote care.
Behavioral Health at Scale: Behavioral health remains one of the highest growth sectors in telemedicine, with mental health services delivered remotely continuing to dominate the telehealth landscape. The demand for virtual mental health services is only expected to increase, especially as stigma decreases and access improves.
Digital Front Doors: Patient access points, whether through apps, portals, or virtual assistants, are becoming the first step in the healthcare journey. Digital front doors will streamline patient routing, ensuring they are directed to the appropriate level of care (virtual or in-person) based on their needs.
According to Mansor, AI technologies will also play a critical role in making these new models more efficient. He states, “By leveraging AI-driven tools, the future of telemedicine will empower healthcare systems to become more data-driven, improving everything from triage to chronic care management.”
Telemedicine has demonstrated its ability to scale, physician adoption in the U.S. surged from 16% to 80.5%, and utilization remains strong, with telehealth claim lines consistently around 5% in late 2024 (commercial claims data).
For investors, CFOs, and CTOs, the real opportunity lies not in funding another telemedicine app but in backing the infrastructure and workflow-native platforms that will shape the future of healthcare. The most promising areas for investment include platforms that:
The macroeconomic potential remains substantial, up to $250B of U.S. healthcare spend could shift to virtual or virtually-enabled care if care pathways continue to evolve.
Building these advanced, integrated solutions requires expertise in both healthcare and technology. AppVerticals, with its experience in creating tailored, scalable healthcare platforms, is well-positioned to support the development of the next generation of telemedicine solutions.
In the U.S., for instance, over 40% of healthcare visits were conducted virtually during the peak of the pandemic. In contrast, adoption is slower in regions with limited access to technology, such as parts of Africa and Southeast Asia.
However, telemedicine adoption is growing globally, with significant increases in Latin America, India, and China as governments and healthcare providers recognize its potential to improve healthcare delivery.
In fact, over 75% of telemedicine users report positive experiences. However, satisfaction can be impacted by technical issues like connectivity problems, lack of personal interaction, or difficulty navigating platforms.
In terms of outcomes, telemedicine has been proven effective for managing chronic conditions, mental health care, and even post-operative care, showing comparable or sometimes superior results to in-person visits.
Amwell: Provides telemedicine solutions to healthcare providers, insurers, and employers, focusing on virtual care and telehealth integration.
Doctor on Demand: Offers video consultations with board-certified physicians and mental health professionals.
MDLive: Provides telehealth services for urgent care, dermatology, and behavioral health.
Livongo Health (now part of Teladoc): Specializes in remote patient monitoring for chronic conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension.
These platforms are known for their robust offerings, technology integration, and ease of use, contributing to the rapid growth of telemedicine services.
Technology Access and Infrastructure: While telemedicine relies on reliable internet access and technology, regions with limited broadband coverage or lower digital literacy may struggle with its adoption.
Clinical Acceptance: Some healthcare professionals are hesitant to fully embrace telemedicine due to concerns over its effectiveness in providing high-quality care, especially in complex cases that require hands-on physical exams.
Reimbursement Issues: Many insurance providers have only partially reimbursed telemedicine services, leading to financial uncertainties for healthcare providers and limited access for some patients.
Data Security and Privacy: As telemedicine involves the exchange of sensitive health information, ensuring strong cybersecurity measures and compliance with data privacy regulations (such as HIPAA) is essential to build trust and prevent breaches.
Discover how our team can help you transform your ideas into powerful Tech experiences.