About Us
I’ve spent years watching enterprise mobile initiatives succeed, or stall, based on one thing: whether leadership treats the app as a business system (security, integration, governance, lifecycle) rather than just a mobile UI.
In practice, enterprise mobile app development is a capital allocation decision: you’re funding faster operations, better compliance, and higher employee/customer throughput, while accepting measurable delivery and security risk.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key factors that define successful enterprise mobile app development, helping you navigate the complexities of security, integration, and governance while maximizing the value of your mobile investment.
Enterprise mobile app development involves creating business apps for large organizations that must:
Work reliably across users, devices, and network conditions
Integrate with core systems (ERP/CRM, IAM, data platforms)
Meet security and compliance standards
As part of a broader mobile app development guide for enterprises, understanding these complexities is crucial for successful implementation. The process includes not just development but a deep integration with existing business systems and robust security frameworks to ensure scalability and compliance.
This is why enterprise apps are inseparable from mobile device management and governance. NIST describes how mobile devices have become permanent fixtures in enterprises and provides guidance on managing and securing devices throughout the lifecycle, covering areas like centralized management and endpoint protection technologies.
CISA reinforces the same operational reality: enterprise-managed mobile devices face threats from a wide variety of sources, and its checklist is explicitly meant to help organizations mitigate vulnerabilities and provide secure mobile access to enterprise resources.
When advising investors, I categorize enterprise mobile apps based on where they create value and where risk is concentrated.
Here are the key types:
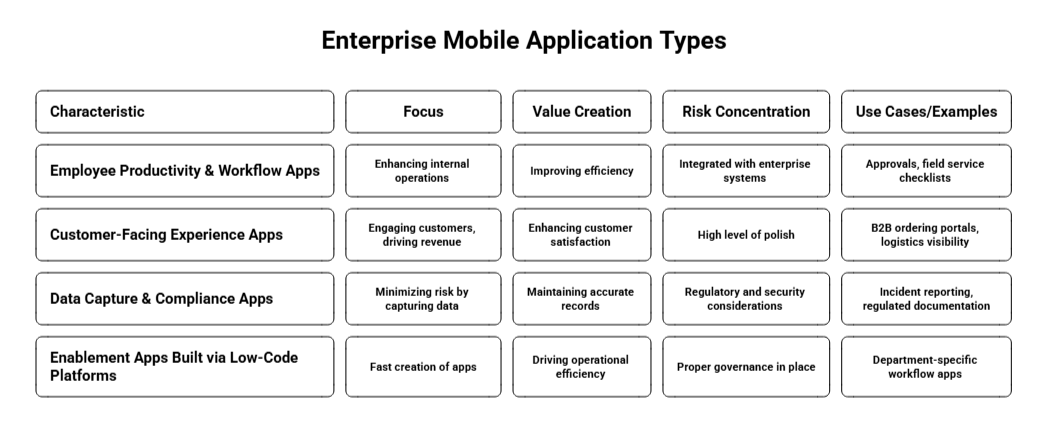
These apps focus on enhancing internal operations and streamlining workflows for employees. They are designed to improve efficiency, reduce manual errors, and ensure consistent execution of business processes.
They are often integrated with enterprise systems like ERP, CMMS, or HRIS, enabling smooth data flow across the organization. Crucial to their design is the ability to function offline and sync seamlessly once connectivity is restored.
Use Cases/Examples:
• Approvals (e.g., expense approvals, leave requests)
• Field service checklists (for technicians in the field)
• Warehouse picking (inventory management and order fulfillment)
• HR self-service apps (employee access to payroll, benefits, etc.)
• Maintenance rounds (automated equipment inspections)
These apps are designed to engage customers, drive revenue, and improve retention. They play a direct role in enhancing customer satisfaction, providing a seamless experience, and fostering loyalty.
These apps typically require a higher level of polish in terms of user experience (UX) design and must be able to scale effectively as user demand increases.
These apps are focused on minimizing risk by capturing critical data and ensuring compliance with regulations. Their primary goal is to maintain accurate records, meet industry standards, and protect sensitive information.
Given the regulatory and security considerations, these apps often become high-stakes, and the security posture can become a key concern at the executive level.
Low-code platforms enable the fast creation of apps without deep technical expertise, allowing departments to quickly build and deploy applications for internal workflows. These platforms are particularly valuable in mature enterprises where there’s a need for rapid iteration and agility.
With proper governance in place, low-code platforms can drive operational efficiency. These platforms often complement custom development, providing a faster route to delivering solutions.
Enterprise mobile apps are crucial for improving operational efficiency, reducing security risks, and ensuring better governance. Here’s the list of key benefits these apps bring to businesses.
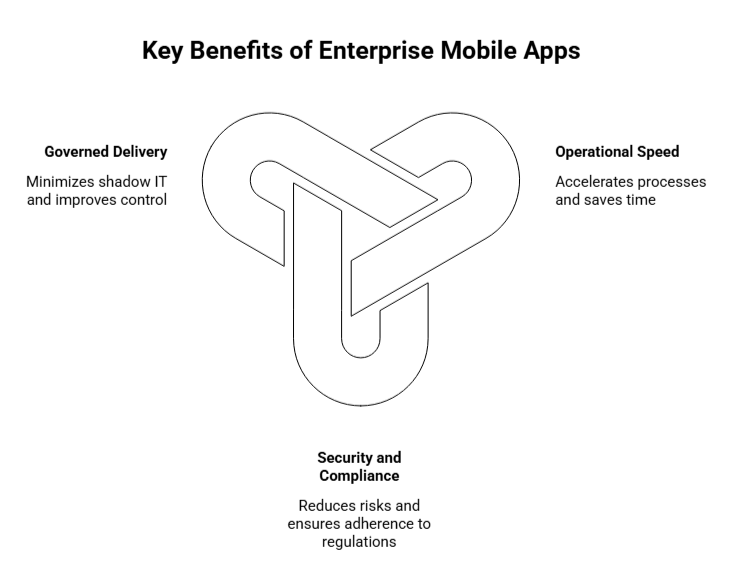
Enterprise mobile apps eliminate latency in approvals, data entry, and coordination, speeding up key processes. Even small time savings in high-frequency tasks can deliver significant operational gains. Instead of massive transformation projects, these apps provide incremental improvements that add up to big results.
For instance, Forrester’s Total Economic Impact (TEI) study of Microsoft Power Platform showed a 224% ROI and $81.7 million in net present value (NPV), with payback in less than six months.
Security breaches don’t just incur IT costs, they cause major operational disruptions. IBM’s 2024 report highlighted an average breach cost of $4.88 million, with costs rising 10% year-over-year.
However, integrating robust security measures during the app development phase can reduce these risks. IBM’s research shows that using AI and automation in prevention workflows led to $2.2 million lower breach costs. Proper security engineering can mitigate potential risks and save costs in the long run.
Don’t leave security to chance. Ensure your enterprise app development is built with robust, proactive security measures from day one.
When business teams lack access to approved mobile solutions, they often resort to unauthorized apps, leading to fragmentation, security risks, and higher maintenance costs.
A structured enterprise mobile program, focused on product, platform, and security governance, reduces this “shadow IT” dynamic. CISA’s checklist emphasizes the need for controlled mobile access, ensuring compliance and reducing long-term risks.
When scoping mobile enterprise app development solutions for large organizations, these features should be considered essential budget drivers, not just “nice-to-haves.”
Here’s a breakdown of the core features that can make or break your project:
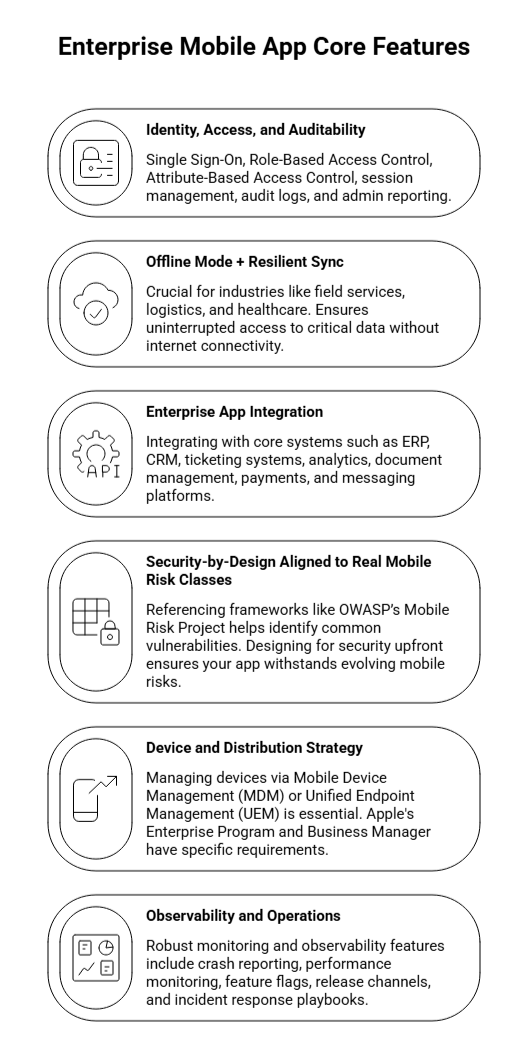
This includes Single Sign-On (SSO), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), session management, audit logs, and admin reporting. These features are often underestimated, but they can significantly impact both the development timeline and security posture. Properly managing identity and access ensures both secure and efficient app usage.
For industries like field services, logistics, and healthcare, offline functionality is crucial. Offline design is often complex and costly but directly influences user adoption. When workers need uninterrupted access to critical data without internet connectivity, ensuring seamless offline operation and resilient synchronization when back online is essential.
Integrating your enterprise mobile app with core systems such as ERP, CRM, ticketing systems, analytics, document management, payments, and messaging platforms is crucial. These integrations drive both the overall project cost and the associated risks. Ensuring smooth data flow across these systems is vital for operational efficiency and reduces the chances of data silos.
Mobile security is non-negotiable. Referencing frameworks like OWASP’s Mobile Risk Project helps identify the common vulnerabilities that arise in mobile app audits and penetration tests—credential handling, authentication, communication, misconfiguration, etc. Designing for security upfront ensures your app withstands the evolving landscape of mobile risks.
For apps distributed internally, managing devices via Mobile Device Management (MDM) or Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) is essential. If you’re distributing on iOS at scale, note that Apple’s Enterprise Program has eligibility constraints and an annual fee of $299 USD.
Alternatively, distributing via Apple Business Manager requires app review but is suitable for private distribution within your organization. These considerations play a crucial role in the operational management and cost of enterprise app deployment.
To keep long-term lifecycle costs predictable, you need robust monitoring and observability features. This includes crash reporting, performance monitoring, feature flags, release channels, and incident response playbooks. These tools help ensure the app remains performant, secure, and easy to manage, reducing costly downtime and improving the overall user experience.
Ready to scale your enterprise app development? Let’s design a solution that maximizes efficiency, security, and user satisfaction.
To keep the enterprise app development process clear and efficient, I ensure it aligns with business goals and is easily communicated to key stakeholders.
Below is a breakdown of the essential stages:
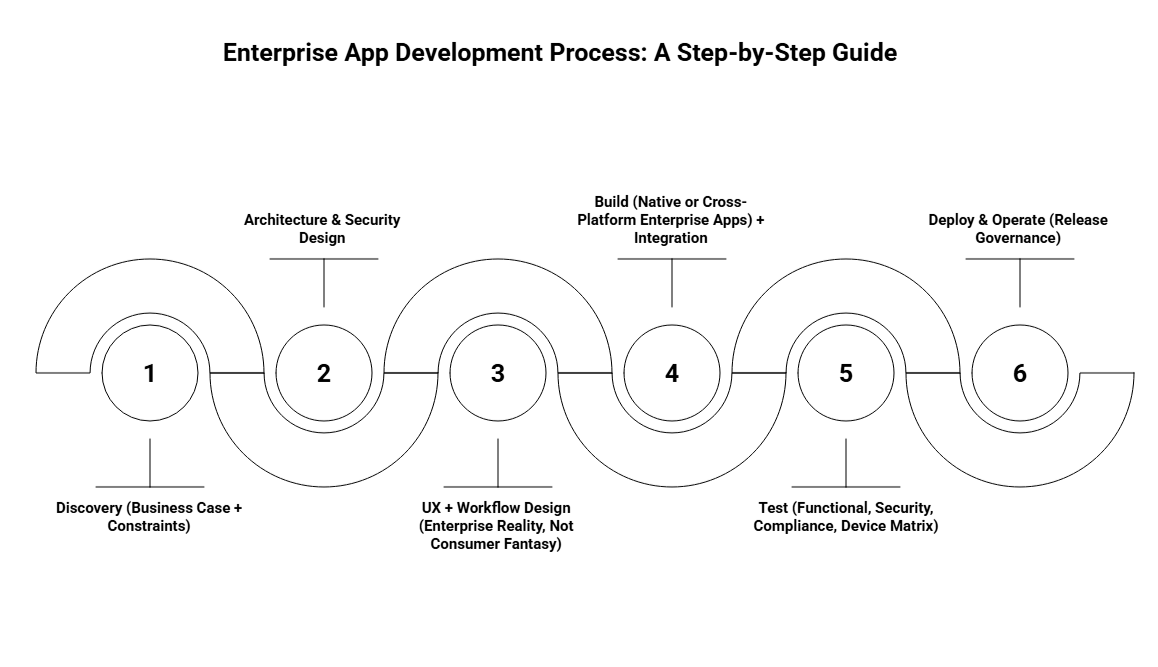
The enterprise app development process begins with defining the business case. Focus on measurable outcomes such as “minutes saved per user per week,” “cycle time reduction,” “error rate reduction,” or “faster revenue realization.” These outcomes become your KPIs and guide the project, ensuring the development aligns with strategic business goals.
The next stage in the enterprise app development process is the architecture and security design. This involves mapping user identity management, data classification, integration boundaries, and the mobile threat model. Referencing NIST’s mobile security guidelines provides a strong foundation for ensuring the app’s security across its lifecycle and management.
Design for real-world conditions in enterprise environments. The enterprise app development process must account for interruptions, workers using gloves, poor connectivity, and strict permissioning. The UX should be intuitive but robust enough to meet the operational challenges faced by enterprise users, not just optimized for consumer-grade experiences.
“One big problem with traditional development platforms is that they lack collaborative features, which is detrimental to the success of any product output. There’s little or no access to crucial data or communication from and with teams handling customer support, administrative, and front-desk duties. That’s a deficit the low-code, no-code technology is fixing. Today, members from R&D, engineering, marketing, sales, and customer support can all work on the same project using a visual drag-and-drop feature. This enables teams to collaborate more effectively and gain valuable insights into customer behavior.”- Gary Hemming, Owner & Finance Director at ABC Finance
The enterprise app development process moves into the actual build phase, whether it’s native or cross-platform development. While cross-platform development can reduce UI duplication, integration, security, and QA remain high priorities. Ensuring seamless integration with existing enterprise systems is crucial for delivering an app that functions smoothly within the business ecosystem.
Testing is a critical stage of the enterprise app development process, ensuring functionality, security, and compliance across various devices. Special attention is needed for Android distribution, as Google’s Play Console now requires new personal accounts (created after November 13, 2023) to undergo a closed test with 12 testers for 14 consecutive days before applying for production access.
The enterprise app development process concludes with deployment and ongoing operation. This stage includes a structured rollout strategy, monitoring, training, and support. For a secure and efficient deployment, CISA’s checklist provides operational hardening guidance, ensuring your app is both secure and well-managed after release.
The cost of enterprise mobile app development is shaped less by the number of screens and more by factors like integration, security, and operational maturity. Mobile app development cost can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the systems being integrated, the level of security required, and the scalability demands of the app.
Here’s a breakdown of the key cost drivers:
Clutch reports the following for enterprise app development projects:
Here’s a detailed cost breakdown:
| Cost Component | What it Includes | Why It Matters to CFO/CTO |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery & Architecture | Requirements gathering, threat modeling, solution design | Prevents rework and sets clear integration scope |
| UI/UX Design | Workflows, prototypes, usability tests | Drives user adoption, reduces training costs |
| App Development | iOS/Android or cross-platform build | Core feature delivery engine |
| Backend & Integrations | APIs, middleware, data sync, audit logs | Often the largest risk driver for enterprise apps |
| Security & Compliance | SSO/RBAC, encryption, testing, hardening | Reduces breach probability and exposure to compliance risks |
| QA & Device Matrix | Automation, regression, performance testing | Prevents production instability and ensures app reliability |
| Deployment & Distribution | MDM/UEM, app store/private distribution | Adds time and tooling costs for rollout |
| Ongoing Ops | Monitoring, incident response, updates | Transforms a “project” into a long-lasting, durable product |
If you’re looking for a more detailed Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) model over three years (covering build, run, and change), I can provide one. I’d just need assumptions about your user count, systems to integrate, offline needs, and security/compliance profile.
In recent discussions, three key trends have consistently emerged as shaping the future of enterprise applications:
Automation and Platform Leverage Over Bespoke Everything
The shift toward automation and platform-based solutions, like low-code platforms, is transforming the economics of enterprise app development. The TEI study for Power Platform shows how organizations are using low-code tools at scale, saving time and avoiding costs. Mobile app development market statistics confirm that low-code and no-code platforms are becoming a cost-effective innovation in the app development industry.
Low-code platforms don’t replace engineering but redefine how backlogs are managed, enabling cost-effective handling of routine tasks.
Security Becomes a Financial Metric, Not an IT Checkbox
Security is no longer just an IT concern; it’s a financial metric. IBM’s breach cost analysis highlights how “security posture” influences investment decisions, especially when mobile apps extend access to sensitive systems. Mobile app download statistics show that security breaches can directly impact user trust, affecting app downloads and long-term usage.
The financial impact of breaches is driving executives to prioritize security in their strategic planning.
Stronger Governance around Mobile Distribution and Testing
As mobile app distribution becomes more regulated, stronger governance is being enforced. Google’s updated testing requirements and Apple’s distribution options, like Apple Business Manager Custom Apps, are shaping release planning in regulated industries.
These changes are ensuring that apps meet compliance standards before distribution, leading to more secure release cycles.
Learn how low-code platforms and automation can drive your enterprise mobile app’s success without the hefty price tag.
Mastering enterprise mobile app development requires a careful balance of security, integration, and governance to maximize operational efficiency and reduce risks. By focusing on the right app types, essential features, and cost drivers, organizations can ensure their mobile initiatives deliver lasting value.
As trends shift towards automation and low-code solutions, adopting the right development approach becomes even more critical. For companies navigating these complexities, partnering with a trusted mobile app development provider like AppVerticals can offer the expertise needed to turn these challenges into successful, scalable solutions.
Let AppVerticals help you navigate complex development challenges and create scalable, secure mobile solutions tailored to your business.
If you’re building a workflow-heavy app with significant back-office integration, cross-platform often works well. For apps that require deep OS-level integrations or have top-tier performance constraints, native development might be justified.
The Apple Developer Enterprise Program is ideal for specific internal distribution scenarios but costs $299/year and has eligibility constraints.
Discover how our team can help you transform your ideas into powerful Tech experiences.