About Us
By 2027, most education apps are turning into AI-powered SaaS products with real-time data pipelines, video, personalization engines, and regulatory obligations.
What I’m seeing across the market:
That’s why teams start hitting the same wall:
slow releases, unstable exam days, exploding cloud spend, security red flags, and engineering teams that can’t keep up.
When six-figure or seven-figure budgets are on the table, the real questions aren’t:
“Can we build this?”
They’re:
Those are the real education app development challenges in 2026, and they’re the difference between a platform that scales and one that quietly falls behind.
In this article, I’ll walk through the actual challenges EdTech teams face when building or modernizing education apps in 2026. Those are the real education app development challenges in 2026, and they’re the difference between a platform that scales and one that quietly falls behind.
Education app development in 2026 is shaped by five forces: user engagement, accessibility, assessment integrity, AI workloads, and enterprise data compliance. Platforms fail when any of these are treated as afterthoughts. Teams that design for personalization, low-bandwidth access, secure assessments, modular cloud architecture, and predictable cost from the start can scale without rewrites, outages, or blocked enterprise deals.
The hardest part of scaling an education app in 2026 is keeping cost, performance, and compliance stable while usage, AI workloads, and data volume explode at the same time. Global EdTech expected to surpass USD 572.08 billion by 2034.
Once a learning platform passes early traction, every design shortcut becomes expensive. I see this constantly when EdTech teams go from tens of thousands of learners to hundreds of thousands or more.
These are the challenges that actually determine whether the platform survives.
The real scaling challenges in 2026
That is what a learning platform really looks like once it scales.
Most teams think they have a performance problem. What they really have is a design problem. By 2026, AI workloads in education software are growing at more than thirty percent per year, and global EdTech usage keeps climbing.
That means platforms are hit with both burst traffic and constant background compute. If those workloads run on the same services that handle exams, logins, and progress tracking, the system becomes unpredictable.
What I see when that happens:
This is why platforms that worked fine in their first growth phase suddenly start missing SLAs, losing enterprise deals, and burning cash.
The teams that scale cleanly do not chase optimization. They change the shape of the system.
What I implement before the next growth wave
When those pieces are in place, scaling stops being a gamble. The platform becomes predictable, costs become manageable, and teams can grow without betting the business on every release.
In 2026, the biggest “learning” challenges in education apps are also the biggest product and platform risks. The most common failure modes are straightforward: learners do not stay engaged, large segments cannot reliably access the product, and assessments lose credibility when integrity is weak. 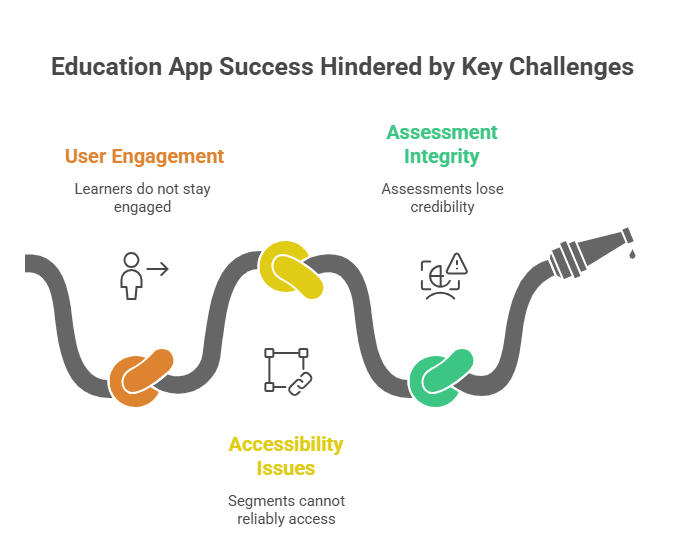
If you build for features without solving these three, growth stalls even if the engineering is strong.
Below is how these challenges show up in real education products, and what experienced EdTech teams design for.
When these three are treated as “product concerns,” teams ship features and still struggle to grow. When they are treated as first class platform requirements, retention improves, enterprise trust increases, and scaling becomes predictable.
In 2026, engagement, accessibility, and integrity are not side problems. They are the foundation that determines whether an education app becomes a durable learning platform.
Institutions using adaptive AI technology report up to 34% improvement in student retention and 28% higher course completion, underscoring the importance of engagement design. In 2026, the fastest way to blow an EdTech budget or miss a launch date is to underestimate how tightly AI, data privacy, and cloud infrastructure are now linked.
Education apps no longer run on simple request and response patterns. They operate continuous data and inference pipelines that process learner behavior, content, and assessments in real time. Every one of those layers adds cost, latency, and delivery risk.
The teams that struggle are the ones that treat AI features, compliance, and infrastructure as separate work streams. In practice, they behave like a single system.
| Driver | What it adds to the platform | How it affects cost and delivery |
|---|---|---|
| AI personalization | Model hosting, inference, embeddings, real time scoring | Increases compute, storage, and operational complexity |
| Student data privacy | Encryption, access control, audit logs, data locality | Adds engineering work and slows releases if not designed early |
| Cloud infrastructure | Auto scaling, observability, backups, failover | Determines whether usage spikes become outages or just higher bills |
When these are designed together, platforms scale predictably. When they are bolted on, teams end up rebuilding parts of the system just to keep it running.
AI has moved from a differentiator to a baseline expectation. Recommendation engines, adaptive quizzes, tutoring bots, and automated grading all rely on constant inference and data processing. What most teams discover too late is that these systems run even when learners are idle.
From what I see in production platforms, every active learner generates:
Multiply that by thousands of concurrent users and the cloud bill no longer scales linearly. It accelerates. Without workload separation, AI traffic competes with core learning flows, creating both cost spikes and latency.
Education apps carry some of the most sensitive data in software. Student identities, performance records, behavioral data, and in many cases minors’ information must be handled under GDPR, FERPA, and regional privacy laws. In 2026, enterprise and institutional buyers run these checks before they sign.
What slows teams down is not regulation itself. It is discovering that the data model cannot support it.
| Requirement | What It Demands | Where Teams Lose Time |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Right to delete, audit trails, data locality | Data scattered across services and backups |
| FERPA | Role-based access and logging | Weak identity and authorization models |
| Enterprise security | Encryption, incident response, traceability | Retrofitting controls into live systems |
When compliance is designed into the architecture, features ship faster. When it is added later, every release becomes a legal and engineering negotiation.
That is why privacy and infrastructure decisions are now some of the biggest drivers of both cost and time to market in education app development.
The biggest risk in modernizing a legacy education platform in 2026 is not choosing the wrong framework. It is carrying yesterday’s assumptions into a system that now has to support AI, mobile scale, real time learning, and strict data regulation.
Most legacy EdTech systems were built for content delivery and basic tracking. They were not designed for continuous personalization, enterprise security reviews, or millions of concurrent users.
In my experience, modernization projects fail when teams underestimate how deeply business logic, data models, and integrations are intertwined.
The result is budget overruns, timeline slippage, and platforms that still cannot scale after months of work.
| Risk Area | What It Looks Like in EdTech | Why It Hurts |
|---|---|---|
| Tightly coupled code | LMS, payments, and reporting share logic and data | Small changes break core flows |
| Legacy data models | Student and progress data hard to migrate | Long cutovers and data loss risk |
| Outdated integrations | SIS, SSO, and content systems lack clean APIs | Features stall and support costs rise |
| Hidden business rules | Years of one-off workflows | Regression bugs and rework |
| Weak test coverage | No safety net for changes | Releases become risky |
These risks compound when AI, analytics, and mobile features are added on top of a brittle core.
Refactoring feels safer because it promises gradual change. In reality, it only works when the system is already modular. When everything depends on the same database and service layer, refactoring just moves complexity around.
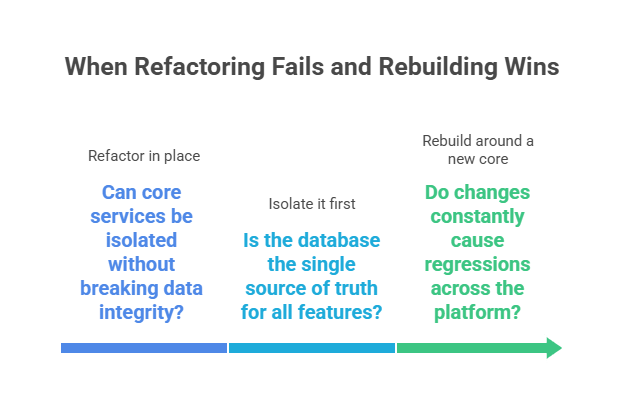
From what I have seen, rebuilding wins when the existing platform cannot be cleanly split into independent parts. It lets teams design for AI workloads, compliance, and scale instead of dragging legacy constraints forward.
Technical debt in education platforms does not just slow engineers down. It directly raises operating cost and business risk.
| Area | Low Debt Platform | High Debt Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Feature delivery | Predictable, incremental | Slow and risky |
| Cloud spend | Scales with usage | Grows faster than users |
| Compliance | Designed into the system | Requires constant retrofits |
| Support load | Low and stable | High and unpredictable |
A majority of educators (about 60%) now use AI-based tools regularly, showing that scalable, performance-aware AI integration is a baseline requirement. High-traffic education platforms in 2026 stay reliable by separating real-time learning, AI workloads, and regulated data into distinct layers.
When everything runs on the same services and databases, performance drops during exams, compliance becomes fragile, and personalization gets expensive.
Modern LMS implementation is no longer just about delivering content. It is about running a distributed system that can handle burst traffic, continuous AI processing, and strict data governance at the same time.
The platforms that survive heavy growth do three things consistently: isolate workloads, control data access, and monitor cost and performance in real time.
That is what allows millions of learners to use the system without outages, audit failures, or unpredictable cloud bills.
Real-time education platforms must handle logins, classes, exams, chat, and video simultaneously. Speed and security come from how requests flow through the system.
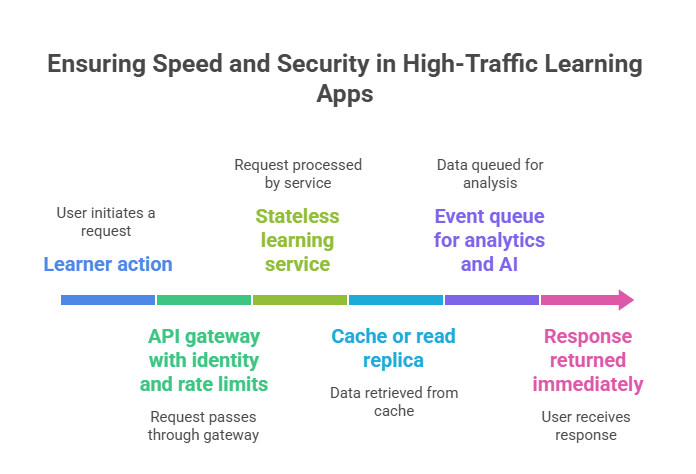
This pattern keeps critical learning paths fast while pushing heavy processing out of the user request. Security is enforced at the gateway and service layer so every call is authenticated, encrypted, and monitored, even when traffic spikes.
Compliance fails when sensitive student data and experimental AI systems live together. In 2026, platforms must support GDPR, FERPA, and enterprise security reviews while still using data to power personalization.
Stack map
This separation allows AI to improve learning without exposing regulated data. It also keeps audits, institutional sales, and enterprise deployments moving instead of getting blocked by security concerns.
The best architecture for education apps in 2026 is one that lets you scale learning, AI, and compliance independently while keeping education app development cost under control.
After working on multiple EdTech platforms, I have seen that the winners are always built on cloud-native, modular systems where no single workload can take down or financially dominate the rest of the platform.
Education apps now run three very different workloads at once: real-time learning, continuous AI inference, and regulated student data.
If those are not isolated and auto-scaled separately, performance degrades and costs spiral. A strong cloud strategy is what keeps growth from turning into technical debt.
Architecture and cloud strategy overview
| Layer | What it handles | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| API gateway | Identity, rate limits, routing | Protects performance and security |
| Core services | Classes, exams, progress | Keeps learning reliable |
| Event and queue layer | AI, analytics, notifications | Prevents heavy jobs from blocking users |
| Data layer | Encrypted student records | Supports compliance |
| Compute layer | Auto-scaling workloads | Controls cloud spend |
This structure allows platforms to absorb spikes, run AI continuously, and still pass audits without rewriting the system.
In early products, monoliths feel fast. At scale, they become the bottleneck.
| Area | Monolith | Microservices |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling | All features scale together | Each workload scales independently |
| AI integration | Competes with core traffic | Runs in its own services |
| Reliability | One failure affects all | Failures are contained |
| Deployment | Large, risky releases | Smaller, safer changes |
Every high-growth education platform I have worked on eventually moved to microservices because it is the only way to scale video, personalization, and assessments without breaking the core experience.
AI changes the cost curve of EdTech. Inference, embeddings, and analytics run constantly, not just when users click.
User growth:
What actually keeps budgets in line:
This is the difference between an education app that scales profitably and one that becomes too expensive to operate, no matter how many users it has.
Get a technical reality check from a team that has built AI-driven EdTech platforms at scale.
Talk to an EdTech Architect
In enterprise EdTech, cost overruns and missed deadlines almost never come from building too many features. They come from uncertainty in architecture, compliance, and integrations.
When large school systems, universities, or corporate training departments buy software, they bring security reviews, data rules, and legacy systems with them.
From my experience working as an edtech app development company on enterprise platforms, this is where projects either stay predictable or start to drift.
What actually drives budget and timeline risk is how much unknown work is hiding behind those requirements.
ROI drivers in enterprise EdTech
| Driver | What It Affects | Why It Moves Cost and Timelines |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture maturity | Development speed | Fragile systems slow every change |
| Security and compliance | Sales cycle | Reviews block deployment |
| Integration scope | Engineering effort | SIS, SSO, and data sync add hidden work |
| Data volume | Infrastructure cost | Grows with users and analytics |
| Team capacity | Delivery reliability | Bottlenecks create delays |
Enterprise buyers reward platforms that feel stable and audit ready. Platforms that feel risky pay for it in both cost and time.
Delays almost always appear in the same places:
Most slip happens in the middle. Data models need changes to satisfy privacy rules. Integrations take longer than expected. Real-world testing exposes edge cases that were invisible in planning.
The more tightly coupled the system, the more each of these ripples through the entire schedule.
The teams that deliver on time build resilience into both their architecture and their staffing.
Execution framework
This is what keeps enterprise EdTech projects predictable. When complexity rises, structure and the right people prevent cost and timelines from getting out of control.
After product-market fit, most EdTech startups discover that demand grows faster than their platform. The challenge is no longer proving that people want the product. It is keeping performance, cost, and delivery stable while usage, data, and AI workloads explode.
From working with startups at this stage, the ones that survive treat scaling as a system redesign, not just a hiring problem.
They invest early in modular architecture, cost visibility, and data boundaries so growth does not turn into technical debt. That is what allows them to onboard more schools, add AI features, and close enterprise deals without constantly stopping to fix the platform.
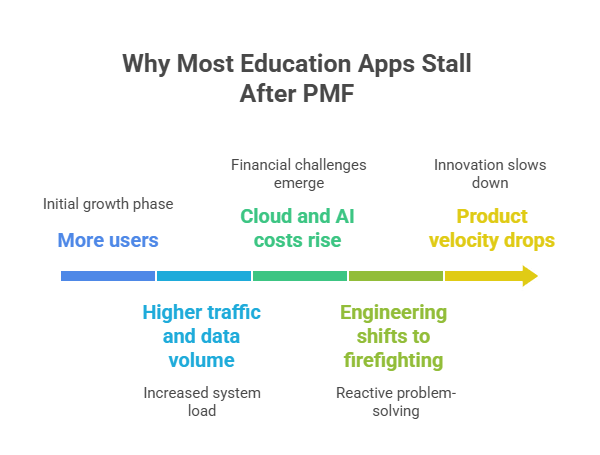
This is the point where many startups stall. The product is validated, but every new feature makes the system more fragile. Without structural changes, growth becomes a liability instead of an advantage.
The teams that keep momentum do not try to do everything with AI. They focus on what moves learning outcomes and revenue.
Lean AI playbook
From experience, this is how small EdTech teams deliver advanced personalization and analytics without losing control of cost or stability.

Cloud spend and compliance now decide whether an EdTech platform scales. If you do not design for both upfront, you pay for it later.
– Kazim Qazi, CEO of AppVerticals
When we started working on Budget University, the challenge was not building another learning portal.
It was building a financial education platform that could support thousands of concurrent learners, protect sensitive personal and financial data, and introduce AI-driven personalization without blowing up infrastructure costs.
The platform was designed around:
That architecture meant the platform could grow without rewrites, pass security reviews from institutions, and support AI-powered learning features as they were introduced.
It is exactly the kind of system you need in 2026 when education apps are expected to behave like enterprise SaaS platforms.
This is the kind of work AppVerticals specializes in: building education platforms that keep working when real users, real data, and real growth hit.
The real challenge in education app development in 2026 is handling everything that arrives once real learners, real data, and real institutions are involved. Engagement drops when learning feels generic. Accessibility becomes critical when users are on weak networks and old devices. Assessment integrity matters when credentials have real value.
At the same time, AI, cloud infrastructure, and data compliance quietly drive cost, risk, and delivery timelines.
Teams that treat these as connected problems, not separate ones, are the ones that build platforms that actually scale.
Get a clear picture of architecture, cost, timelines, and risk from engineers who have delivered real learning platforms.
Start an EdTech Strategy Session
Discover how our team can help you transform your ideas into powerful Tech experiences.